
Precision Die Casting
in Malaysia
Welcome to MORELUX, your trusted partner and expert in precision die casting services in Malaysia. With a strong commitment to quality, innovation, and customer satisfaction, we offer industry-leading die casting solutions tailored to meet your unique manufacturing needs. Whether you require complex components or high-volume production, MORELUX has the expertise and technology to deliver exceptional results that exceed expectations.
Your Expert For Precision Die Casting Services In Malaysia
At MORELUX, we specialize in precision die casting—a process known for producing intricate and high-strength metal parts with excellent dimensional accuracy. Our team of skilled engineers and technicians dedicate themselves to delivering the best die casting services. We leverage advanced machinery and strict quality control to ensure consistent and reliable production for your projects.
Engineering Services
Our engineering services form the backbone of our precision die casting capabilities. From the initial design consultation to prototype development, we work closely with you to optimize your part design for manufacturability and performance. Our engineers utilize cutting-edge CAD and simulation software to predict and solve potential manufacturing issues before production begins. This attention to detail reduces lead times, cost, and waste, ensuring your parts meet all specifications.
- Tooling Design
- CNC Machining Services
- Surface Finishing Solutions
- Assembly & Integration
Mechanical Equipment
MORELUX operates a fleet of state-of-the-art die casting machines that support both hot chamber and cold chamber processes. Our equipment ranges in clamping force, enabling us to produce components of various sizes and complexities. We maintain our presses regularly and upgrade our tooling to guarantee precision and efficiency. Our advanced mechanical capabilities allow us to handle high-volume runs while maintaining tight tolerances.
- 280 to 2000 ton of high pressure die cast machines
- Automatic deburring and tumbling systems
- Vacuum-Assist Casting Units
- 3-axis, 4-axis and 5-axis CNC machines
Quality Control
Quality is at the heart of everything we do at MORELUX. We implement rigorous quality control protocols at every stage—from raw material inspection to final product testing. Our in-house laboratory performs dimensional checks, material analysis, and mechanical testing to ensure parts meet industry standards and customer requirements. With ISO certified processes and continuous improvement practices, we are committed to delivering flawless die cast components every time.
- Smart Scope
- CMM
- Spectrometer
- X-Ray Scanner
Types of Die Casting Processes by MORELUX
MORELUX offers various die casting methods to suit different materials and product specifications.
We select the most appropriate process based on your project’s requirements for precision, volume, and cost.
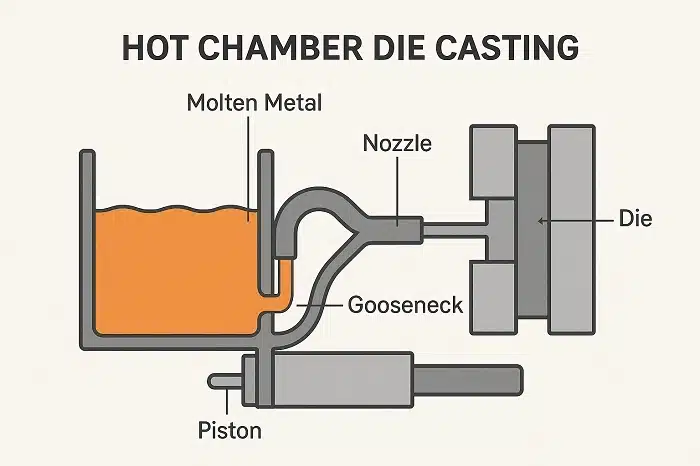
Hot Chamber Die Casting
Hot chamber die casting is ideal for metals with low melting points like zinc. In this process, the metal is melted inside a furnace connected to the die casting machine, enabling faster cycle times and higher production rates. MORELUX uses hot chamber die casting for small to medium-sized, complex parts requiring excellent surface finishes.
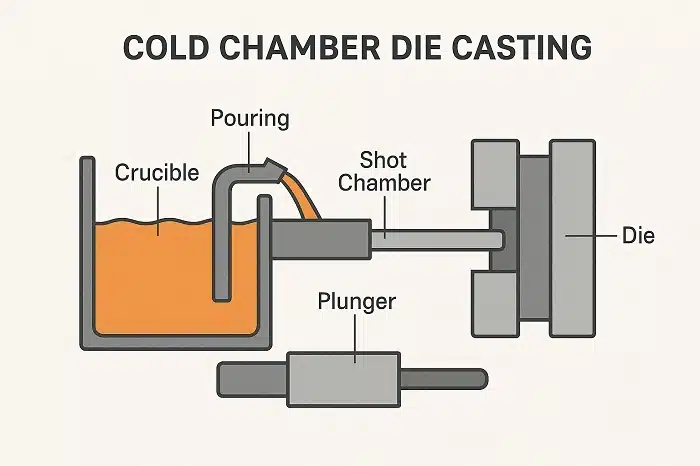
Cold Chamber Die Casting
Cold chamber die casting is suitable for metals with higher melting points, such as aluminum and brass. Here, molten metal is poured into a cold chamber and then forced into the mold. Though slower than hot chamber methods, cold chamber die casting delivers high strength and dimensional accuracy. MORELUX ensures parts meet strict performance standards.
Choosing the Right Metal for Your Die Casting Project
MORELUX provides expert guidance on material choice based on part function, strength requirements, and budget.
Aluminium Die Casting
Aluminium is a lightweight, corrosion-resistant metal with excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. It is widely used in automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries. MORELUX’s aluminium die casting services produce durable parts with great surface quality and structural integrity.
- A360
- A380
- A383
- A413

Zinc Die Casting
Zinc offers high dimensional stability and is perfect for producing intricate shapes with thin walls. It is cost-effective and provides good corrosion resistance. MORELUX’s zinc die casting capabilities are ideal for consumer products, hardware, and electrical components.
- Zamak 3
- Zamak 5
- ZA-8
- ZA -27

Brass Die Casting
Brass combines excellent strength and machinability with an attractive, corrosion-resistant finish. It is widely favored for making decorative parts, plumbing fittings, and musical instruments due to its durability and aesthetic appeal. MORELUX’s brass die casting ensures precision and consistency in every batch.
- C260
- C360
- C280
- C385

Precision Die Casting Surface Finishing
Surface finishing is an important step to enhance the appearance, durability, and functionality of die cast parts.
MORELUX provides a wide range of finishing options to meet your project’s design and performance needs.
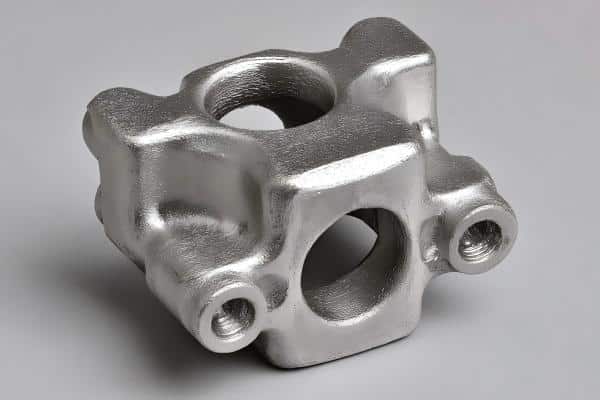

As Cast
The AS cast finish refers to the metal’s natural surface immediately after the casting process. It is generally smooth with minor texture irregularities, making it suitable for parts that will undergo additional machining or coating treatments later.

Polishing
Polishing creates a bright, reflective finish on die cast parts, significantly enhancing their overall appearance and surface smoothness. This process is ideal for decorative or exposed surfaces that require a visually appealing and refined look, improving both aesthetics and functionality.
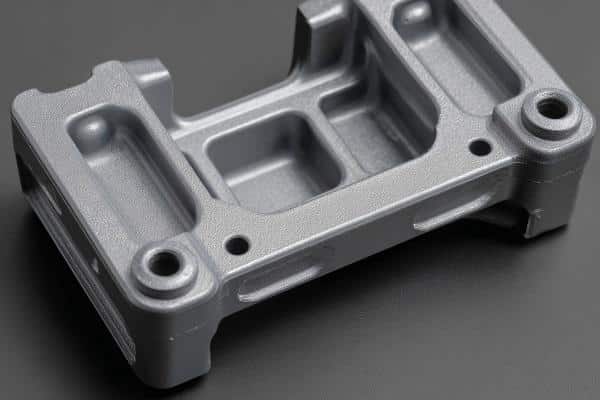

Anodizing
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that enhances the corrosion resistance of metal surfaces while adding vibrant colors. This treatment creates a durable, protective oxide layer, making the metal more resistant to wear and ideal for use in harsh and demanding environments.
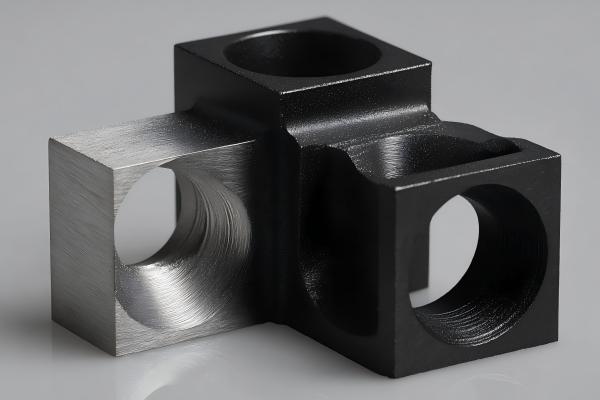

Brushed Finish
A brushed finish creates fine, parallel lines on the surface, adding a textured appearance that helps reduce glare and minimizes visible fingerprints. This type of finish is commonly used in electronics and hardware products to enhance both aesthetics and durability.
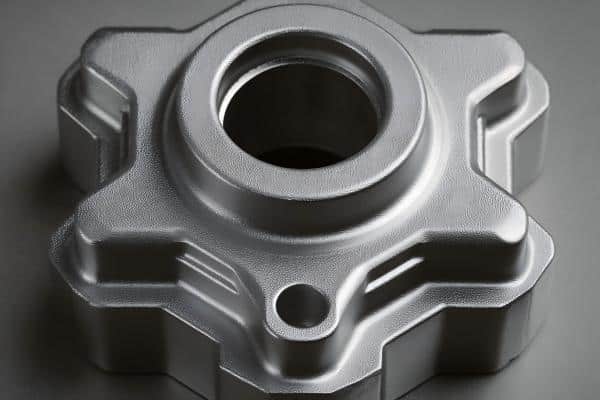

Sand Blasting
Sand blasting effectively removes surface impurities and old coatings, while creating a matte or satin texture. This process significantly improves the adhesion of new coatings and enhances the overall surface quality before the finishing treatment is applied.

Powder Coating
Powder coating involves spraying a dry powder onto a surface, which is then cured by heat to create a durable and corrosion-resistant finish. This process produces colorful coatings that protect parts from chemicals, moisture, and abrasion, extending their lifespan significantly.
Applications of Pressure Die Casting
MORELUX excels in providing precision pressure die casting services for these diverse industries. With advanced technology and skilled expertise, MORELUX delivers high-quality parts tailored to specific industry needs. Whether it is automotive, electronics, medical, or aerospace, MORELUX guarantees precision, durability, and excellent surface quality, helping clients bring high-performance products to market.
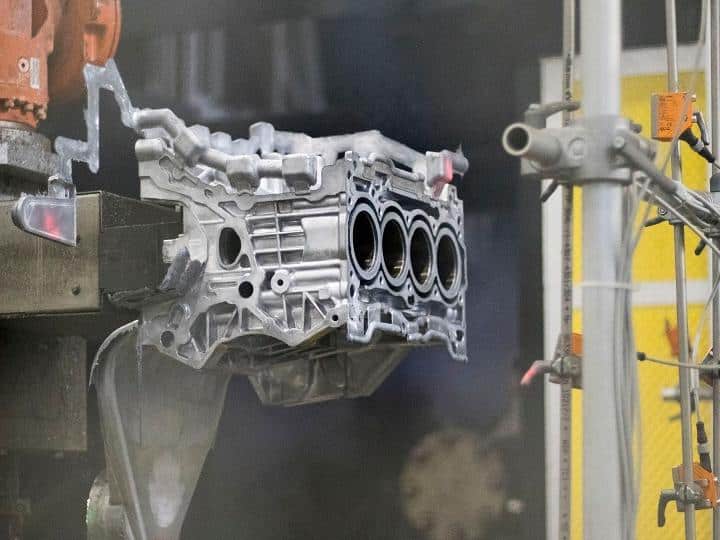
- In the automotive industry, pressure die casting produces precision engine parts, transmission components, and structural elements critical for vehicle performance and safety. These parts require tight tolerances and durability, which this method can reliably provide.
- For consumer electronics, pressure die casting enables the creation of small, detailed, and aesthetically pleasing parts for smartphones, laptops, and televisions. The smooth finish and accurate dimensions help improve both the product’s look and functionality.
- In industrial equipment, this process is used to make tough and durable parts like pumps, valves, and motor housings. These components must withstand harsh conditions and heavy use, which pressure die casting ensures through its strong and precise output.
- Furniture and lighting industries also benefit from pressure die casting by producing intricate parts for lighting fixtures and furniture hardware. The method allows the creation of strong yet visually attractive components.
- Electrical and plumbing sectors use this technology to manufacture reliable electrical enclosures and plumbing fittings, such as faucets and valves, requiring precision and durability.
- In the medical field, pressure die casting is essential for producing precise instruments and components that ensure reliability and hygiene in medical devices.
- The aerospace industry depends on this process to produce lightweight and durable engine and structural parts. These components meet strict performance and safety standards necessary for aircraft.
Looking For a Trustworthy Die Casting Manufacturer in Malaysia?
Let’s Talk About Your Next Precision Die Casting Project
With MORELUX, you gain a trusted partner capable of producing precise, high-quality die cast parts tailored to meet your industry’s demanding standards. Contact us today to explore how our expertise can support your next project and help drive your success.
FAQs of Pressure Die Casting
What is die casting process?
Die casting is a metal casting process characterized by forcing molten metal under high pressure into a mold cavity called a die. The die is typically made of hardened steel and designed to withstand high temperatures and pressures. This process is commonly used with non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, zinc, magnesium, copper, lead, and their alloys. The die casting process consists of several main steps:
- Die Preparation: The die is created and prepared, often using CAD and CNC machining. It is coated with a releasing agent or lubricant to help release the cast part and control temperature.
- Metal Preparation: The metal is melted in a furnace. For hot chamber die casting, the melting occurs inside the casting machine; for cold chamber die casting, it happens outside and the molten metal is ladled into the machine.
- Metal Injection: The molten metal is injected under high pressure (between 1,500 and 25,400 psi) into the die cavity to quickly fill the mold before solidification begins.
- Cooling and Solidification: The molten metal cools and solidifies inside the die while the pressure is maintained.
- Ejection: Once solidified, the mold opens and ejector pins push the cast part out.
- Trimming: Excess material such as flash is removed for a clean and finished product.
Die casting is widely used for producing complex metal parts with high precision and excellent surface finish. It is especially suited for high-volume production of small- to medium-sized castings due to low incremental costs after initial die creation. The two main types of die casting are hot chamber, suitable for metals with lower melting points, and cold chamber, suitable for metals with higher melting points. This process offers fast cycle times, accuracy, consistency, and the ability to produce parts with tight tolerances.
What are the tolerances for die casting?
Die casting tolerances vary depending on factors such as the material, size, complexity, and application of the parts, but here are some general guidelines:
- For aluminum die casting, typical linear tolerances are around ±0.12mm (±0.005 inches) for small dimensions (up to about 18mm / 0.7 inches). For larger parts, tolerances expand gradually: up to ±0.27mm (±0.011 inches) for dimensions up to 30mm, and up to about ±1.6mm (±0.063 inches) for very large parts over 1000mm (39 inches) in size.
- Surface flatness tolerance for aluminum die casting is about ±0.025mm (±0.001 inches), and tolerance for parting lines is around ±0.25mm (±0.01 inches).
- Standard die casting tolerances generally fall in the range of ±1% to 2% of the nominal dimension. For small die-cast parts below 25mm, tolerances can be as tight as ±0.005 inches (±0.13mm).
- Precision die casting can achieve even tighter tolerances: typically ±0.001″ to ±0.002″ for zinc, and ±0.002″ to ±0.004″ for aluminum parts.
- According to SFSA and ISO 8062 standards, die casting achieves tolerance grades roughly CT4 to CT6, indicative of precision casting.
- Wall thickness is generally controlled between 2.5 to 4mm, with minimum radius for fillets around 1mm, to maintain structural integrity and meet tolerance requirements.
What are die casting design considerations?
Die casting design considerations focus on ensuring the part’s manufacturability, functionality, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here are the key design considerations:
- Fillets and Radii: Use fillets and radii to create smooth transitions between surfaces to prevent stress concentrations and improve strength and durability. Fillets should generally not be less than 1 mm.
- Wall Thickness: Maintain uniform wall thickness throughout the part. Uniform thickness helps ensure even solidification, reduces porosity, and improves casting quality. Avoid varying thicknesses that can cause weaknesses or defects.
- Ribs and Coring: Add ribs to provide structural support and help maintain strength while reducing weight. Ribs also help metal flow and cooling.
- Holes and Windows: Design holes/windows carefully to prevent defects and ensure proper metal flow.
- Draft Angles: Include appropriate draft angles for easier ejection from the die and to prevent damage. Typical draft angles are about 0.5° for zinc and 1°-2° for aluminum.
- Parting Lines: Consider the parting line’s location to avoid complicated steps or features that increase tooling and casting costs.
- Tolerance Zones: Allow for achievable tolerances based on metal choice. Tight tolerances increase cost and complexity; use lenient tolerances where possible.
- Material Properties: Consider the specific properties of the metal being used, including fluidity, solidification, and mechanical requirements.
- Ejection: Ensure that the part can eject easily from the die without surface damage or flash formation.
- Design for Manufacturability (DFM): Optimize design to minimize secondary operations and machining costs.
- Consistent Solidification: Design so that metal solidifies evenly to reduce shrinkage and defects.
- Avoid Sharp Edges: Use fillets to avoid sharp edges that can cause stress risers and cracks in the die.
