
Die cast engine block technology changed car making by making it faster and easier. Companies said they got better accuracy, smoother surfaces, and could make parts quickly. This led to breakthroughs in automotive die-castings manufacturing.
- Making complicated shapes got simpler, so new designs were possible (a benefit also seen in electronics die-castings).
- Car companies made less waste and used less energy, which helped the environment.
Now, car makers use die casting to make strong, light parts, often through aluminum die-casting, that help cars use less gas. As more people want these parts, die cast engine blocks keep changing how cars are made.
Evolution of Engine Block Manufacturing
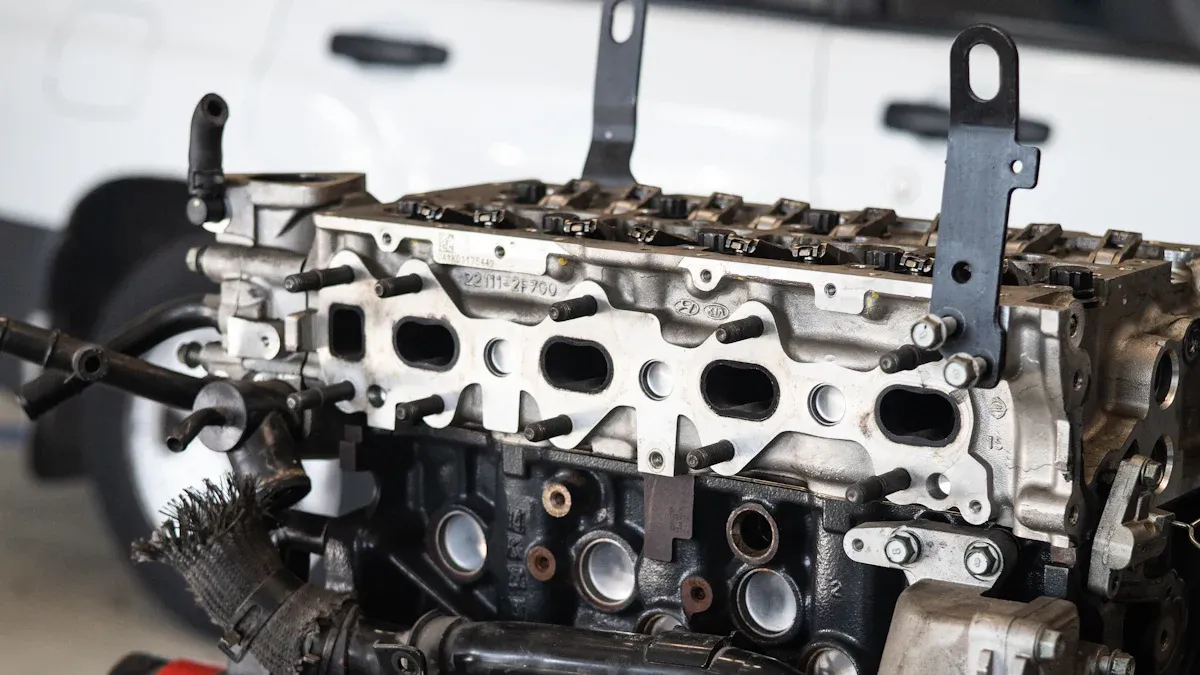
Early Die Casting Applications
Before die casting, people used older ways to make engine blocks.
- Sand casting used sand molds to shape hot metal. This worked for small amounts and let people make different shapes. But it made rough surfaces and needed more work to be exact.
- Machining, like CNC machining, cut metal blocks into shape. This way made strong and exact parts but took longer and used more stuff.
- Both ways had problems with smoothness, speed, and making the same part every time.
Die casting made things better. At first, car makers used it for small parts like carburetor bodies. Die casting gave smoother surfaces and better accuracy. This helped companies make more parts faster and waste less. Because of this, engine block making started to change a lot.
Shift to Aluminum Die Cast Engine Block
Switching from small die cast parts to big aluminum engine cylinder blocks was a big step for car makers. Aluminum had many good things compared to cast iron.
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Material Properties | Aluminum is light, strong, and does not rust easily. It also moves heat well, so it works great for engine blocks. |
| Weight Reduction Impact | Aluminum is about one-third as heavy as steel. This makes engines and cars lighter. Cars use less gas when they weigh less—about 6-8% better for every 10% weight drop. |
| Manufacturing Advances | New die casting ways let people make big, tough, and tricky aluminum engine cylinder blocks. |
| Performance Benefits | Aluminum engine cylinder blocks cool down fast and stay strong under pressure. This helps engines work better and last longer. |
| Environmental & Industry Trends | Aluminum is easy to recycle and makes less pollution when made. This helps car makers build greener cars. |
Moving to aluminum engine cylinder blocks taught car makers a lot. They learned how to make parts that are strong and easy to build. They made sure aluminum worked well and stayed tough. Die casting for aluminum engine cylinder blocks now lets companies make lots of parts, save gas, and pollute less. These changes keep making engine block building better for the future.
Advancements in Die Casting
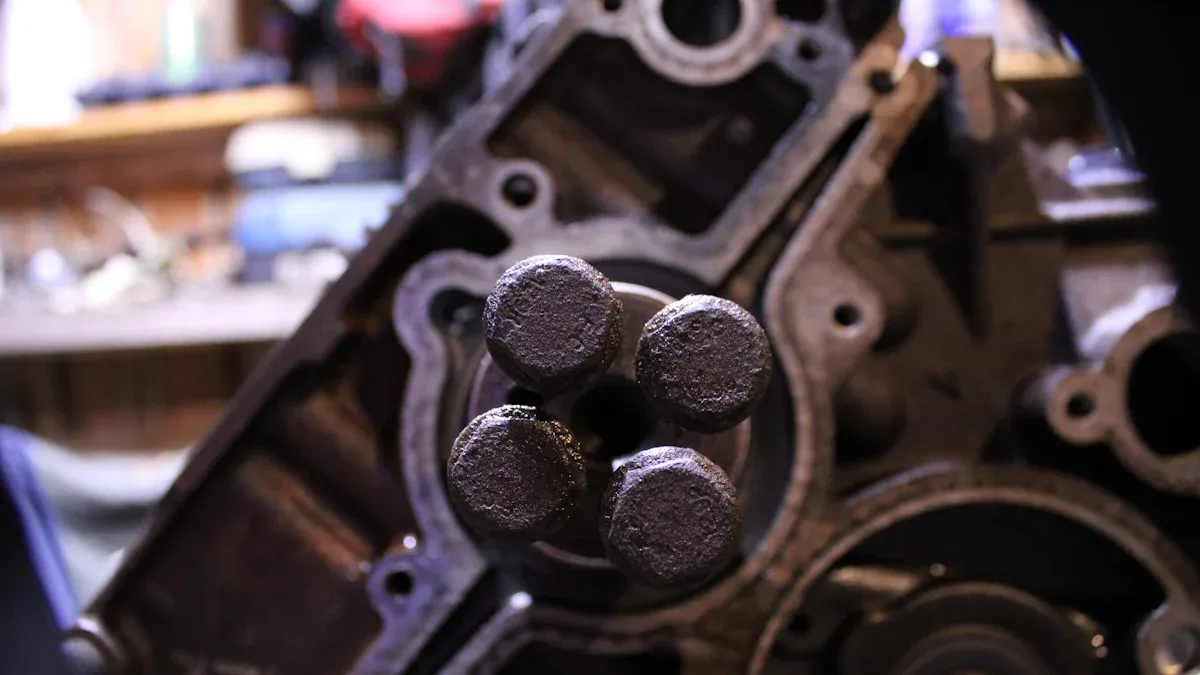

Acurad and Low Iron Alloys
The Acurad process was a big change for die casting. Engineers studied how heat moved during die casting. This helped them keep the right temperature. It stopped cracks and weak spots from forming. They also used flow and fill modeling. This let them see how molten metal moved. Engineers made sure the metal filled every part of the mold. There were no gaps or bubbles left behind.
Acurad let people use low-iron aluminum alloys like A356 and A357. These alloys did not stick to the dies. So, makers could heat-treat them to make them stronger. The process used a double shot piston design. This design pressed on the metal as it started to harden. It helped stop holes and weak spots inside the engine block. These new ideas made engine blocks stronger and more reliable.
| Technological Advancement | Description | Effect on Engine Block Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Stable filling and directional solidification with fast cycle times | Controlled metal flow and solidification | Reduced turbulence and air entrapment, improving casting integrity |
| Large gate at lowest die cavity point | Gate design to minimize turbulence | Prevents gravity-related defects and turbulence |
| Secondary (inner) plunger inside main plunger | Feeds shrinkage porosity | Reduces shrinkage defects and porosity in castings |
| Bottom fill system requiring stable flow-front | Smooth metal flow into die cavity | Enables casting of low-iron aluminum alloys without soldering to die |
| Ability to cast heat treatable low-iron aluminum alloys (A356, A357) | First die casting process to cast these alloys successfully | Allows heat treatment, meeting military specifications, improving mechanical properties |
| Patented double shot piston design (indirect squeeze casting) | Applies pressure after partial solidification | Enhances casting density and reduces porosity, leading to higher quality castings |
Note: The Acurad process helped make engine blocks stronger, lighter, and more reliable.
Pressure Die Casting Methods
Pressure die casting changed how fast and well engine blocks could be made. Machines push molten aluminum into a mold using high pressure. This fills every small space and removes air bubbles. The metal cools and hardens in just seconds. Factories can make many parts very quickly.
| Feature | Pressure Die Casting | Gravity Die Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Production Speed | Very high; molten metal solidifies in seconds or milliseconds, enabling fast manufacturing | Slower; molten metal fills mold by gravity, resulting in slower production |
| Precision | High; capable of producing accurate, complex castings with thin walls and smooth surfaces, reducing secondary machining | Lower; produces thicker walls and rougher surfaces, requiring more machining |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, often without pits or imperfections | Rougher surface finish |
| Machining Allowance | Small; less secondary machining needed | Large; more machining required |
| Suitability for Mass Production | Ideal for long production runs and high quantities with consistent quality | Less suitable for mass production; better for smaller runs or simpler parts |
| Complexity of Parts | Can produce intricate and precise components | Limited to simpler shapes |
Modern die casting uses very high pressure, sometimes up to 1000 bar. This spreads molten aluminum evenly in the mold. The mold fills fast and makes parts with tight tolerances, sometimes as close as ±0.1 mm. Fast cooling makes the metal dense and strong. Factories can make thousands of engine blocks that look the same. The surfaces are smooth and there are few defects. These new ways help car makers build engines that last longer and work better.
- High pressure fills tiny spaces and removes bubbles, so there are fewer defects.
- Fast mold filling helps the metal take the right shape, making parts more accurate.
- Quick cooling makes the metal grains small, which makes engine blocks stronger.
- Good die design controls how metal flows and stops air pockets.
- The quality stays the same and meets strict rules.
Computer-Aided Engineering
Computer-aided engineering, or CAE, brought new ideas to die casting. Engineers use special software to see how molten metal moves and cools in the mold. They can spot problems like air pockets or weak spots before making any parts. This lets them fix the design or process to stop defects.
CAE helps engineers make engine blocks that are light but still strong. The software shows the best way to pour the metal and where to put cooling channels. Experts say CAE now does up to 90% of the design work for die casting. This means less time and money spent on real tests.
A case study on engine blocks made from AA7075 alloy showed CAE could find and fix defects like cold shuts and air bubbles. By picking the right temperatures and cooling, engineers made engine blocks with no defects. The study proved CAE saves time and money and makes better parts.
Tip: CAE helps engineers make engine blocks that are strong and not too expensive.
These new die casting ideas have changed how car makers build engine blocks. With better control, more accuracy, and fewer defects, modern die casting makes parts that fit today’s cars.
Impact of Die Cast Engine Blocks on Vehicle Design
Lightweight and Fuel Efficiency
Die cast engine block technology changed how engineers design cars. Aluminum makes these blocks much lighter than cast iron ones. They are about 40-55% lighter. This helps make the whole car weigh less. When cars are lighter, they use less fuel. For every 10% drop in weight, fuel use goes down by about 6-8%.
Car companies now make cars that meet tough fuel rules. Lighter engine blocks also help cut down on pollution. Die casting lets engineers make tricky shapes. This means they can design smaller, better engines. These engines use less gas and make less pollution.
- Die cast engine blocks help make cars lighter, safer, and easier to drive.
- The process cuts down on waste and helps recycling, which is good for the planet.
- Better fuel use saves drivers money and helps nature.
Note: Lighter cars with die cast engine blocks can go farther on the same tank of gas.
Enhanced Engine Performance
Engineers have seen big gains in engine performance with die cast engine block technology. The process makes parts that fit together very well and have smooth surfaces. This helps engines run better and last longer. Aluminum moves heat away fast, so engines stay cool and work harder without getting too hot.
Engineers use special computer tools like CAE and FEA to design strong, light engine blocks. These tools let them test ideas before making real parts. This means engines can be smaller but still powerful and use less fuel.
| Defect Type | Defect Rate Before Optimization | Defect Rate After Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| Leakage Box | 41.67% | 0% |
| Shrinkage Defect | 37.50% | 0% |
The table shows how new die casting ways have cut down on problems. Fewer problems mean engines last longer and work better. For example, a new diesel engine block made this way weighed 15% less than old ones. It could last up to 2 million kilometers before 10% of engines had trouble. This shows better engine performance and longer life go together.
- Die cast engine blocks help engines have more power for their weight.
- Engines can run hotter and at higher pressure, so they work better.
- Better engine performance means cars speed up faster and handle better.
Complex Component Integration
Die casting lets engineers design engine blocks with tricky shapes. They can put many parts into one solid piece. This means fewer bolts and joints, so engines are lighter and stronger. The process makes sure parts fit just right.
- Engineers can add cooling channels, mounts, and other things right into the engine block.
- The process helps factories use robots and make parts fast, which saves money and makes better parts.
- Shapes that were too hard to make with cast iron are now easy with die casting.
Car designers now make small engines that fit in tight spaces. This lets them try new car designs, like lighter frames and better layouts. Putting many things into one die cast engine block helps car makers build cars that are lighter, work better, and last longer.
Tip: Making complex parts in one piece means fewer parts, less weight, and better gas mileage.
Environmental Benefits of Die Casting
Recyclability and Resource Efficiency
Die casting helps the environment by making recycling easier. Aluminum is the main metal in die cast engine blocks. It can be recycled many times and still stay strong. Car makers take old engine blocks and melt them to make new ones. This saves raw materials and cuts down on waste.
- Recycling aluminum uses less energy than making new aluminum.
- Factories use closed-loop systems to keep using the same materials.
- Less waste means fewer landfills and a cleaner planet.
Aluminum’s ability to be recycled helps car makers reach their green goals. It also lowers the carbon footprint for each car. Using recycled aluminum saves money and protects nature. This helps the car industry stay sustainable for a long time.
Emissions Reduction
Die casting helps lower pollution from cars. Aluminum engine blocks are much lighter than steel or iron ones. Lighter cars use less fuel and make less pollution. If a car is 10% lighter, it can use 6-8% less fuel. This helps car makers follow strict pollution rules.
The table below shows how die casting helps cut pollution:
| Benefit | Impact on Emissions |
|---|---|
| Lighter engine blocks | Less fuel used, fewer emissions |
| Better heat flow in engines | Improved efficiency, lower emissions |
| Advanced die casting methods | Fewer defects, less waste |
| Use of recycled aluminum | Lower carbon emissions |
New die casting methods, like high-vacuum and semi-solid die casting, use less energy to make parts. These ways can cut energy use by up to 10%. Making aluminum parts uses more energy than iron at first, but cars save more energy over time. Die casting and recycling together help the car industry become more eco-friendly.
Future Trends in Die Cast Engine Block
New Alloys and Materials
Car makers keep looking for better materials for engines. High-performance aluminum-silicon alloys are now very important. These alloys use nanotechnology to make them about 30% stronger. They also help the engine stay cool and last longer. Many companies use high-pressure die casting to shape these alloys. This lets them make engine blocks with thin walls and tricky shapes. Some parts are now over 30% lighter because of this process. The table below shows what makes these new materials special:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| New Alloy Developed | High-performance aluminum-silicon alloy for new energy vehicles |
| Performance Improvements | Higher yield and tensile strength, better heat flow, lighter weight, stronger with nanotech, improved wear and corrosion resistance |
| Manufacturing Method | High-pressure die casting for complex shapes and thin walls |
| Industry Impact | Lighter engine blocks, better fuel efficiency, longer vehicle range |
| Additional Notes | Advanced testing and quality control support market growth |
These new ideas help car makers follow tough fuel and pollution rules. They also help electric cars go farther on one charge. Car makers try to recycle more and use materials wisely to keep up with new trends.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
New ways of making things are changing how engine blocks are built. 3d sand printing is a big new idea. This method builds sand molds one layer at a time. It lets engineers change designs fast and make custom parts. 3d sand printing helps make engine blocks with shapes that old ways cannot do. It also cuts down on waste and makes things faster.
Additive manufacturing, like 3d sand printing, means factories do not need heavy tools. This saves energy and makes less pollution. Now, engine blocks can have special channels inside and be lighter. Automation, AI checks, and 3d sand printing all help make parts faster and better.
Experts think die casting will keep growing fast. The market may grow by 7.5% each year until 2032. Pressure die casting will still be the main way to make lots of engine parts. More people want light materials as electric cars get more popular. Factories will use more robots, digital twins, and 3d sand printing to meet these needs.
Car companies get ready for the future by using strong alloys, new ways to build, and green ideas. They teach workers new skills and follow strict rules for quality. These steps help them fix problems like holes in parts, high tool costs, and tricky engine shapes.
The future of die cast engine blocks depends on new ideas. New alloys, 3d sand printing, and smart factories will shape the next engines. Companies that try these things will be leaders in making better, greener cars.
Die cast engine block technology changed how cars are made. Car makers now make light and exact parts. These parts help cars use less gas and make less waste. New machines, AI, and better alloys help car makers meet tough green rules. Companies buy machines that save energy and use recycled stuff. This helps the planet. As more cars become electric, die casting will still be important. It helps build cars that are good for the earth and work well.
FAQ
What is a die cast engine block?
A die cast engine block is a main engine part made by forcing molten metal into a mold. This process creates a strong, lightweight block with smooth surfaces. Car makers use it to build engines that work better and last longer.
Why do car makers use aluminum for engine blocks?
Aluminum weighs less than iron or steel. It resists rust and moves heat well. These features help cars use less fuel and run cooler. Aluminum also makes recycling easier, which helps protect the environment.
How does die casting help the environment?
Die casting uses less energy and creates less waste than older methods. Factories can recycle aluminum many times. This process lowers pollution and saves natural resources. Car makers meet green goals by using die cast engine blocks.
Can die cast engine blocks handle high power engines?
Yes. Modern die casting creates strong engine blocks that handle high pressure and heat. Engineers use special alloys and computer tools to make sure these blocks stay tough, even in powerful engines.
What new trends are shaping die cast engine blocks?
Car makers now use advanced alloys, 3D printing, and smart robots. These trends help build lighter, stronger, and more complex engine blocks. The industry keeps changing to meet new rules and customer needs.
