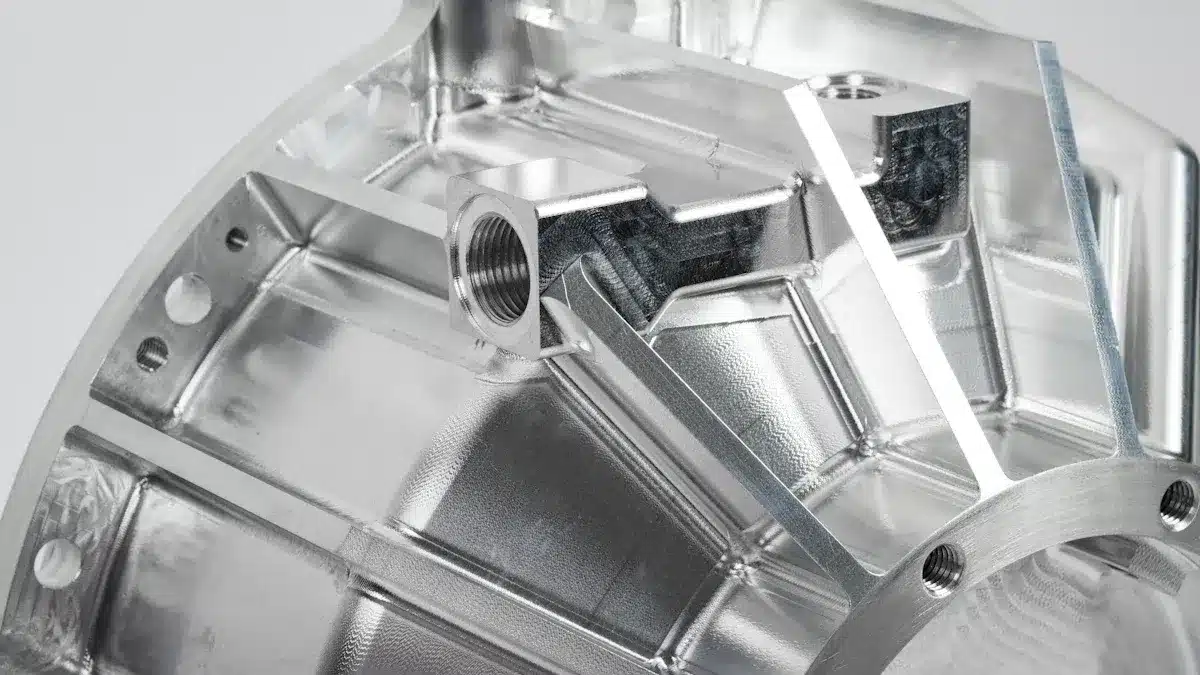
Automotive Die Casting
Automotive die casting is a manufacturing process where molten metal is injected under high pressure into a mold cavity, called a die, to produce complex, high-precision metal parts. The process is widely used for metals such as aluminum, copper and zinc alloys, which offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios.
By leveraging the benefits of lightweight materials, precision engineering, and cost-effective production, die casting empowers automakers to create safer, greener, and more advanced vehicles.
If you are looking to enhance your automotive manufacturing capabilities, partnering with MORELUX can unlock new opportunities and drive your business forward in this competitive market.
Ready to transform your automotive components with cutting-edge die casting solutions? Contact us today to learn how we can help you accelerate innovation and quality in your production line!
Benefits of Die Casting in the Automotive Industry
The future trends of die casting in the automotive industry focus on lightweighting, electrification, and automation.
Lightweight materials like aluminum and magnesium are increasingly used to reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency.
The rise of electric vehicles drives demand for specialized die-cast parts such as battery enclosures and motor housings.
Automation and Industry 4.0 integration enhance precision and production efficiency.
Die casting also supports the growing complexity of electronic components in autonomous vehicles by enabling intricate, precise parts.
- Fabrication of Lightweight Components: Reduces vehicle weight, improving fuel efficiency and lowering emissions.
- Increased Durability and Strength: Produces strong, wear-resistant parts that enhance vehicle lifespan.
- Enhanced Automation and Flexibility: Allows mass production of complex shapes with high precision.
- Efficient Production Cycles: High-speed, high-pressure casting shortens manufacturing time.
- Precise, Complex Parts: Enables internal features and thin walls without extra machining.
- Recyclability and Environmental Benefits: Uses recyclable materials like aluminum, supporting sustainability goals.
MORELUX: Experienced Automotive Die Casting Manufacturer
MORELUX is an experienced manufacturer specializing in automotive die casting components, with over 20 years of expertise. Morelux operates vertically integrated manufacturing facilities with extensive in-house capabilities, including mold design and fabrication, die casting, precision CNC machining, finishing, powder coating, and local assembly.
Why Choose MORELUX for
Automotive Die Casting
Experience and Expertise
MORELUX has decades of automotive die casting experience, ensuring precise, reliable parts with expert engineering and industry knowledge.
Metal & Casting Capability
Choose from millions of possible combinations of materials, finishes, tolerances, markings, and certifications for your automotive castings order.
Strict Quality Control
MORELUX implements rigorous quality control measures. We are ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485, IATF 16949:2016, and AS9100D certified.
Our Automotive Die Casting Services

1. Mold Manufacturing
The mold, or die, is usually made from hardened steel designed to withstand high temperatures and pressures. The process starts with a CAD design of the mold, which is then precisely manufactured using CNC machining to ensure accurate dimensions and durability for repeated use.
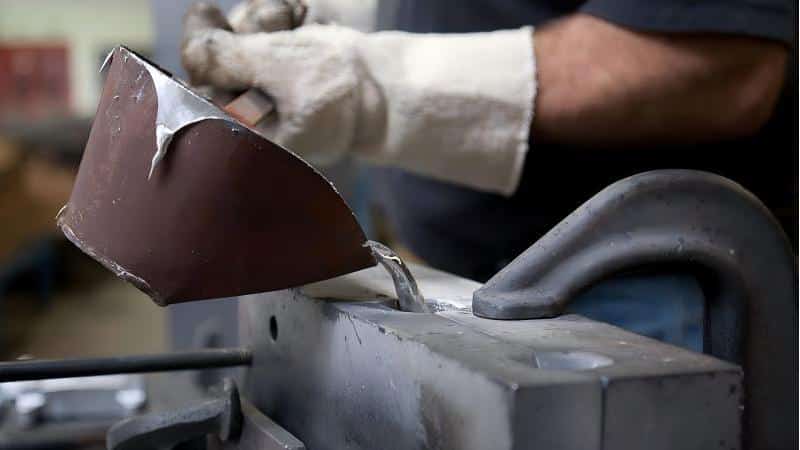

2. Die Casting
The molten metal is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure, either via hot chamber or cold chamber die casting methods. The metal fills the mold and solidifies quickly. Hot chamber suits low melting point metals like zinc; cold chamber suits higher melting metals like aluminum.
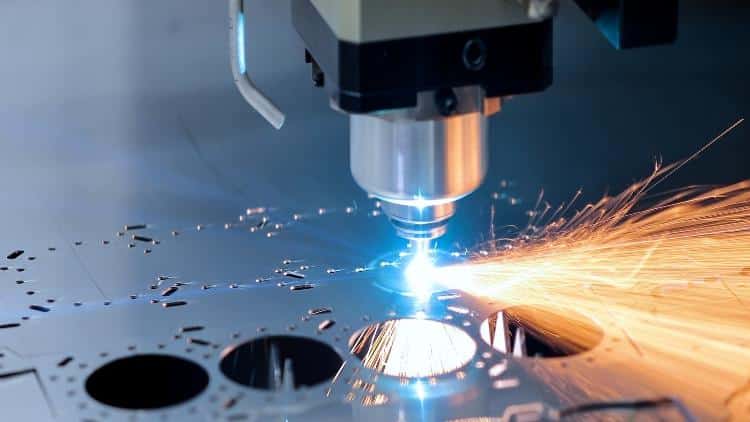

3. CNC Machining
After die casting, CNC machining is often employed to achieve precise tolerances. It also allows the addition of intricate features and detailed modifications that are otherwise impossible through casting. This additional step significantly enhances the dimensional accuracy, improves surface quality.
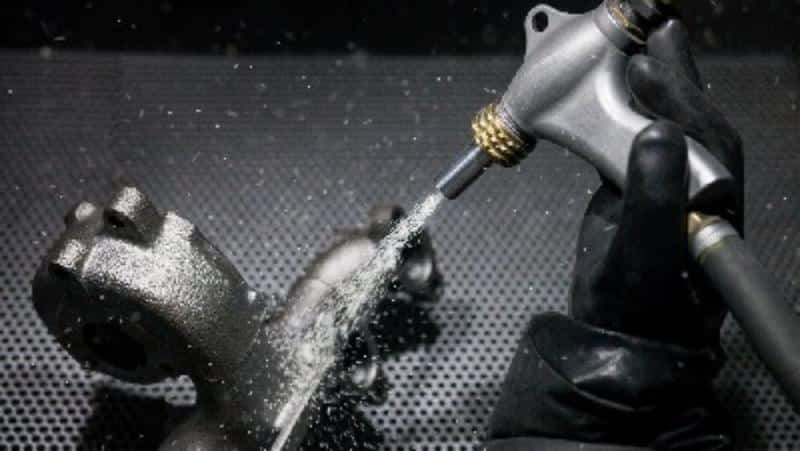

4. Surface Finishing
Surface finishing improves the part’s durability, corrosion resistance, and appearance. Common finishing techniques include anodizing, powder coating, plating, polishing, and painting. Trimming is also performed to remove excess metal such as flash or sprues, ensuring a clean final product.
Metals Used for Die Casting in the Automotive
MORELUX provides expert die casting solutions primarily using aluminum alloys optimized for automotive structural and functional parts, supported by copper alloy and zinc alloys for specific applications, all aimed at meeting the evolving demands for lightweight, durable, and cost-effective automotive components.
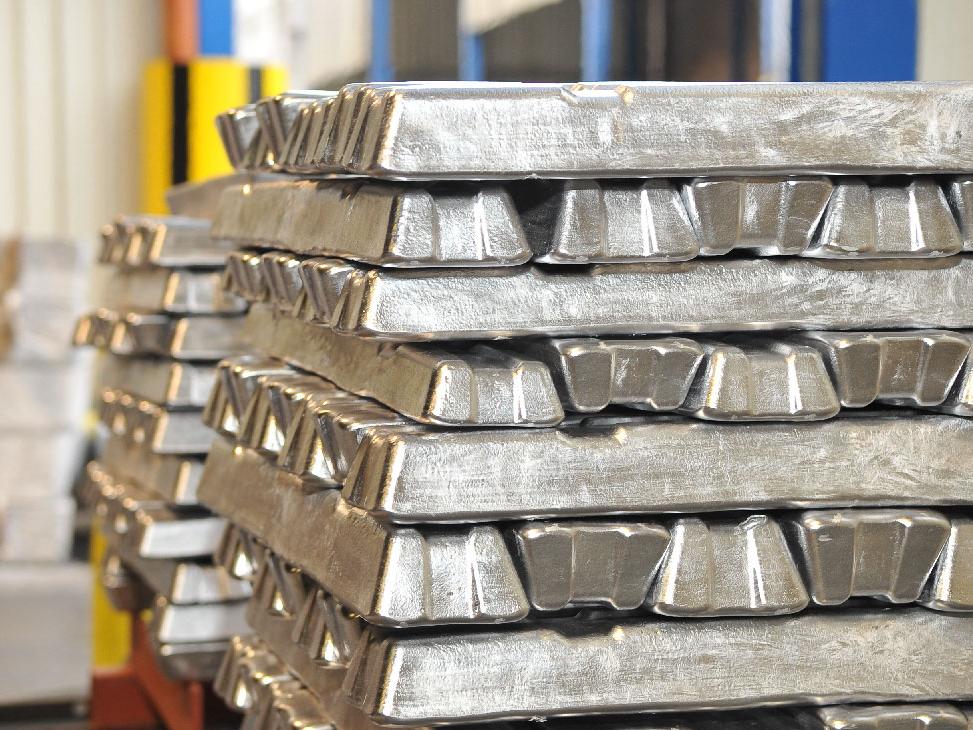
Aluminum Die Casting for Automotive
- Aluminum alloys are widely used due to their lightweight, good corrosion resistance, high dimensional stability, and good mechanical properties.
- Common aluminum die casting alloys include AA 380 (with about 9% silicon and 3.5% copper), AA 360 (low copper), and AA 390 (high silicon for wear resistance in engine cylinders).
- Aluminum is cast at around 650 ºC and is favored for parts that require complex shapes and thin walls while maintaining strength and thermal conductivity.
- Aluminum die castings are common in automotive engine components, housings, and structural parts where weight reduction is critical.


Zinc Die Casting for Automotive
- Zinc alloys are known for their high melt fluidity, allowing for close tolerances and thinner walls than aluminum.
- Zinc is alloyed with about 4% aluminum to increase strength and hardness.
- Zinc die casting is performed at a lower temperature (~425 ºC), enabling fast filling, cooling, and ejection, which results in short cycle times.
- Zinc alloys are used for precision parts such as gears, sprockets, and connector housings in automotive applications.
- Zinc’s ease of casting and good impact strength make it economical for small, complex parts.
Copper Alloy Die Castings in Automotive
- Copper alloys are valued for their high hardness, excellent wear resistance, high thermal and electrical conductivity, and corrosion resistance.
- Despite copper’s high melting point making die casting more challenging, copper alloys allow for complex geometric shapes and reduce costs compared to subtractive methods like CNC machining.
- Copper die cast parts in automotive are often used in heat exchangers, radiators, bushings, brackets, and electrical connectors where thermal management and electrical conductivity are crucial.
- The copper die casting process typically uses cold chamber or vacuum die casting to handle the high melting point and improve quality by reducing porosity.
Applications of Die Casting
in the Automotive Industry
MORELUX is committed to delivering innovative die casting solutions that support the automotive industry’s drive toward lighter, stronger, and more efficient vehicles. Our expertise across a broad spectrum of automotive components—from engine parts to advanced electronic housings—positions us as a trusted partner for OEMs and suppliers worldwide.
- Engine Components
- Transmission Parts
- Suspension and Structural Parts
- Exterior and Interior Body Parts
- Electronic and Sensor Housings
- Fuel Intake Parts
- Connectors for Autonomous Vehicles
- Power Steering and Braking Systems
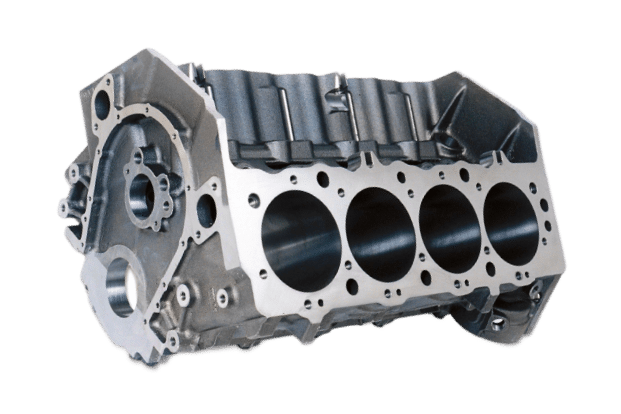
Engine Components
We manufacture engine blocks, cylinder heads, pistons, and other critical engine parts using aluminum die casting. These parts benefit from aluminum’s lightweight and excellent thermal properties, enhancing engine efficiency and performance.
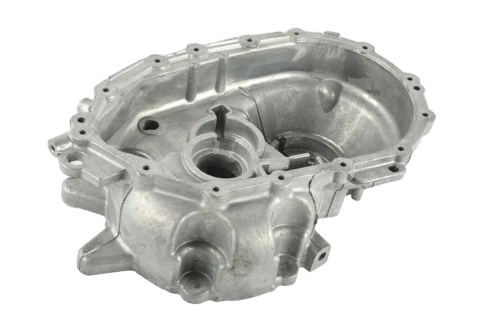
Transmission Parts
Our advanced die casting process produces high-quality transmission cases and housings with precise dimensions and exceptional strength, ensuring seamless and reliable transmission operation in various automotive and industrial applications.
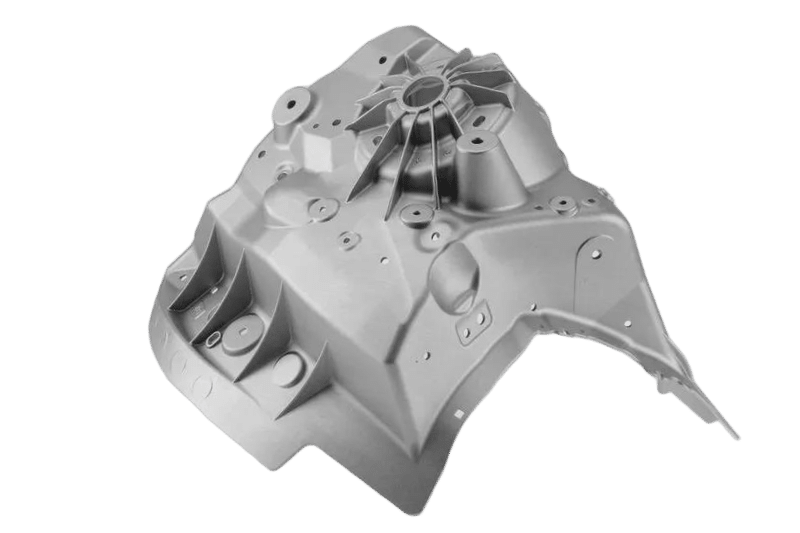

Suspension and Structural Components
MORELUX specializes in supplying high-quality suspension arms, brackets, frames, and strut mounts designed to reduce overall vehicle weight while maintaining excellent structural integrity, thereby significantly enhancing fuel economy and vehicle handling performance.

Exterior and Interior Body Parts
Die casting is a manufacturing process used to create various exterior and interior body parts such as door handles, mirror brackets, steering wheel frames, dashboard trims, and HVAC system parts, effectively combining aesthetic appeal with functionality and strong structural integrity.
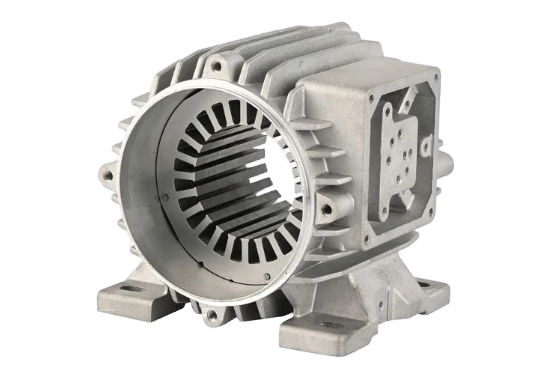
Electronic and Sensor Housings
Electronic and Sensor Housings Applications include housings for sensors, airbags, lidar, telematics equipment, and electronic covers for gearboxes and motors . Die casting ensures precise formation for optimal fit, performance, and durability .
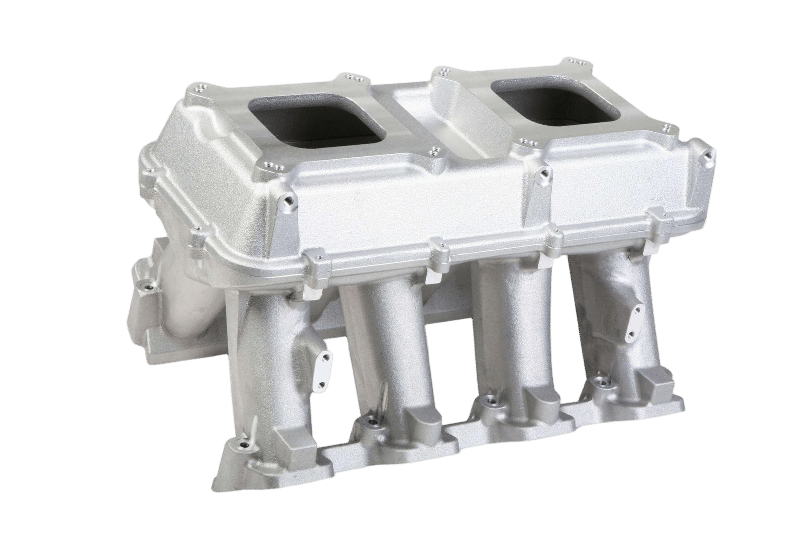
Fuel Intake Parts
We provide lightweight and corrosion-resistant fuel intake components designed to support efficient and reliable fuel delivery systems, ensuring optimal engine performance and durability in various demanding operating conditions.
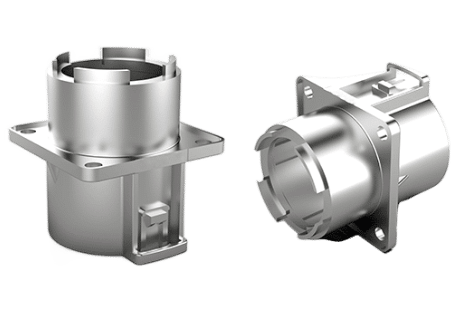
Connectors for Autonomous Vehicles
Recognizing the rapidly evolving future of automotive technology, MORELUX specializes in manufacturing highly reliable and durable connectors that are essential components for the safe and efficient operation of advanced autonomous vehicle systems worldwide.

Power Steering and Braking Systems
Our extensive die casting expertise includes the precise production of high-quality components specifically designed for power steering and braking systems, which are critical in ensuring both vehicle safety and optimal performance on the road.
FAQS about Automotive Die Casting
What are the requirements for manufacturing die castings for modern automotive parts?
The requirements for die castings in modern automotive parts focus on lightweight, high-strength, complex, and precise components for today’s vehicles, including electric and hybrid models.
- Material Selection: Aluminum, zinc, and magnesium alloys are used for their light weight and strength. Aluminum is most common for its balance of weight, durability, and recyclability. Zinc offers corrosion resistance and flexibility. Magnesium is very light but less used.
- Die Casting Processes: Hot chamber die casting is for low-melting metals like zinc and magnesium, suitable for small to medium parts. Cold chamber die casting is for high-melting metals like aluminum, making strong, complex parts.
- High-Pressure Die Casting: This main method creates complex, strong parts with good surfaces and low porosity.
- Design and Simulation: Accurate part size, shape, and material choice are vital. Advanced design and simulation reduce defects.
- Mechanical and Physical Needs: Parts must be strong, precise, and resistant to corrosion, with good conductivity for electric vehicles.
- Manufacturing Considerations: The process must be cost-effective, support large-scale production, and ensure high quality.
What are the costs that need to be considered for automotive die casting components?
These factors collectively define the overall cost structure of automotive die casting components. The key costs to consider for automotive die casting components include:
- Material Costs: Cost varies by alloy type (aluminum, zinc, copper), material waste (8-10%), and melting losses.
- Tooling and Mold Costs: Includes mold design complexity, number of cavities, machining, materials, and maintenance.
- Production Volume: Higher volumes reduce per-unit costs by spreading tooling and setup expenses.
- Labor and Overhead: Skilled labor for operations (deburring, inspection) and overhead like energy and facility maintenance impact costs.
- Post-Processing: Secondary operations such as machining, surface finishing, anodizing add to total cost.
- Part Complexity: Complex geometries, thin walls, undercuts increase tooling and production difficulty, raising costs.
What types of defects can occur in automotive die castings and how to deal with them?
The following are common defects in automotive die castings. Proper mold design, temperature control, and regular maintenance are key to managing these defects.
- Porosity: Small holes caused by trapped gas or air, weakening the part. Prevent by controlling gas venting and mold filling speed.
- Cracks: Caused by stress or uneven cooling. Reduce by optimizing cooling and casting parameters.
- Flash: Excess metal at mold parting lines due to poor clamping or die wear. Fix by ensuring proper clamping and die maintenance.
- Cold shuts: Lines where molten metal fails to fuse, caused by low temperature or slow flow. Avoid by adjusting temperature and injection speed.
- Soldering and drags: Sticking of metal to the die causing surface defects. Prevent by maintaining die surface and proper mold release agents.
- Shrinkage: Voids from metal contraction during solidification. Minimize by uniform wall thickness and thermal control.
Which quality standards are followed to produce automotive castings?
The production of automotive castings follows stringent quality standards and inspection methods to ensure safety, performance, and reliability. Key quality standards and practices include:
- IATF 16949: This is the global automotive quality management system standard, focusing on defect prevention, continual improvement, and reducing variation and waste in the supply chain. It is widely adopted by automotive casting manufacturers to meet customer-specific requirements and regulatory compliance.
- ISO 9001:2015: Provides a systematic approach to quality management, ensuring consistent delivery of castings that meet customer and regulatory requirements. Many foundries producing automotive castings maintain ISO 9001 certification to ensure repeatability and continuous improvement.
- NADCA Standards: For die castings, NADCA provides dimensional tolerance guidelines, alloy property data, porosity classification, and design best practices that are critical for automotive components.
- ASTM Standards: Relevant ASTM standards such as ASTM B557 (tension testing of aluminum alloys), ASTM E155 (radiographic inspection), and ASTM E94 (radiographic examination procedures) are used to verify mechanical properties and detect internal defects in castings.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques like X-ray inspection, ultrasonic testing, and magnetic particle inspection are routinely employed to detect internal flaws without damaging the components, ensuring structural integrity of safety-critical parts.
- Dimensional Accuracy and GD&T: Use of Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs), laser scanning, and geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) ensures that castings meet precise dimensional and geometric requirements, critical for assembly and function.